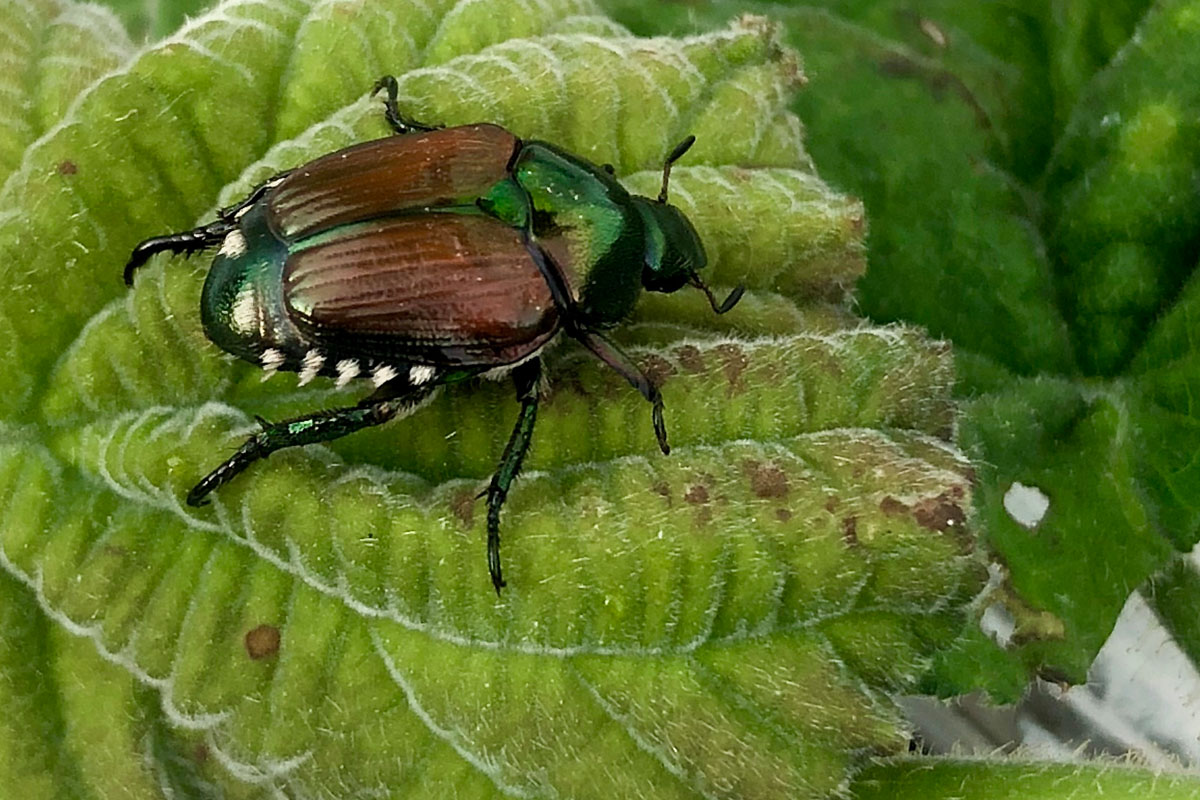
japanese beetle life cycle colorado
As adults Japanese beetles can be found feeding and mating on foliage and flowers of their host plants. The first beetles out of the ground seek out suitable food plants and begin to feed immediately.

Effective Management Remains Elusive For Beetle That Eats Almost Anything
A Japanese beetle life cycle is completed in one year.

. Japanese Beetles have one generation per year and adult females lay 40-60 eggs in the soil that hatch into grubs about 10 days later4. However some adults may be found into September. Colorado was originally thought to be protected from invasive Japanese beetle.
The Japanese beetle was first introduced into Colorado in the early 1990s from nursery stock purchased in the mid-western United States. The egg-larva-pupa-adult life cycle begins when the adult beetles emerge from their winter home spent as larva and pupa below turf grass. The adult beetles normally emerge during the last week of June through July.
Biology and Life Cycle one-year complete life cycle from egg larva pupa adult. Japanese Beetle in Colorado. Beetles quickly skeletonize the foliage by chewing in between leaf veins leaving a lacy appearance.
In Colorado adult beetles emerge from the soil mid to late June with peak emergence occurring in mid to late July. Following their life cycle will help in understanding when and what control products to use. Adults emerge around June or July and immediately begin to feed mate and lay eggs.
Adult beetles are most numerous in July but may persist well into August. Larvae and eggs of Japanese beetle need at least 10 inches of soil moisture to thrive. Leaves turn brown and prematurely fall off.
Around the very end of June or early in July the adult beetles will emerge from your lawn and start showing up on your plants. The female beetle digs about 10 cm into the soil several times over a period of about two weeks each time laying eggs in small batches. After this spring feeding period during the third summer of its life cycle the grub.
The adult females then lay eggs in the soil which hatch and the larvae start chomping down on your grass. Unfortunately our love for lush green lawns comes gives them just the nursery theyre looking for. Japanese beetle larvae overwinter as third instars 10 to 15 cm deep moving down in the soil to avoid freezing.
In the southeast grubs will pupate in May with adults emerging in June starting the process over. Adult Japanese Beetles feed on a wide range of broadleaf plants and weed but at the grub stage this lawn-damaging insect will also feed on a wide variety of plant roots including ornamental trees and shrubs. The larvae of Japanese Beetles are white grubs with a distinct V-shaped series of bristles on their rasters.
Eggs hatch one to two weeks later and the small larvae feed on the nearby roots. The first beetles out of the ground seek out suitable food plants and begin to feed. Adult beetles can be detected in traps until early September depending on weather conditions.
Through winter the Japanese beetle in the larval stage a white grub found within soil. Grubs live in the soil feeding on plant roots. It can also cause damage to fruits gardens and other crops.
Japanese beetle has a one year life cycle. Adults may begin to emerge from the soil in early June and are usually most abundant in early summer from late June through early August. Larvae that have matured by June pupate and the adult beetles emerge from the last week of June through July.
Japanese beetles have a one-year four-stage life cycle like butterflies but JBs take one full year. Adults usually emerge in June females begin egg laying until September. Damage caused by grubs may not be noticeable until after severe lawn damage becomes obvious.
The adult female beetle burrows into the soil laying up to 60 eggs. Please take a few minutes and complete the Japanese Beetle Plant Survey to help with a regional plants list of plants they like and dont like. Observing Japanese beetles feeding on plants is quite common since the adult beetle feeds on about 300 species of trees shrubs ornamental and fruit trees in addition to vegetable crops.
The best way to control adult beetles is to make a preemptive strike in the spring well in advance of the adults emerging. White grubs are becoming a major problem for lawns in Colorado due to irrigation. The egg larva and pupa life cycle stages develop underground and unless soil is removed or dug into these life stages will not be seen.
Scientists and experts were caught off guard by the ability of the pest to establish itself in our region thinking that Japanese beetle an insect that likes moisture and humidity would never become a problem in the semi-arid Colorado climate. The progressive life stages of the Japanese beetle during that period are egg larva white grub pupa adult. These early arrivals begin to release an aggregation pheromone odor that attracts additional adults.
Control Strategies Adult Control Option 1. Cultural Control Hand Picking. Japanese beetles life cycle begins in our lawns Female adult beetles each lay 40 to 60 eggs in their lifetime.
Adult beetles are most active in the heat of the day and are voracious feeders on ornamental and agricultural plant. Each female lays up to 60 eggs as an. The life cycle of this pest takes about a year to complete.
Knowing a little about this insects life cycle will help in managing and minimizing the damage. They emerge from the soil in June and are most actively feeding through August. A white grub is the immature larval form of a scarab beetle such as a European chafer or Japanese beetle.
The well-watered root zones of our turf grass. On warm sunny days the new beetles crawl onto low growing plants and warm for a while before taking flight. What is the life cycle of the Japanese beetle.
Prevention Mitigation and Management of Japanese Beetle Prevention Mitigation and Management of Japanese Beetle. With understanding of the Japanese beetles life cycle and the management options that can be used during the larval and adult stages well continue to enjoy our landscape plants and gardens for many years. Japanese beetle has a life cycle that takes one year to complete.
Orkin Termite Treatment Pest Control Exterminator Service. The Japanese beetle is an extremely destructive pest causing severe damage to turf landscape and ornamental plants. Colorado was originally thought to be protected from invasive Japanese beetlePopillia japonicacolonization and establishment due to our semi-arid climate.
Japanese beetles go through a one-year life cycle but if you have a yard you care about the real joy with beetles comes in the second half of the summer in Colorado. The grubs feed until October and will remain inactive until spring March April when they start to feed again. The Japanese beetle has a one year life cycle.
In late summer the eggs hatch into grubs.
Japanese Beetle Management In Minnesota
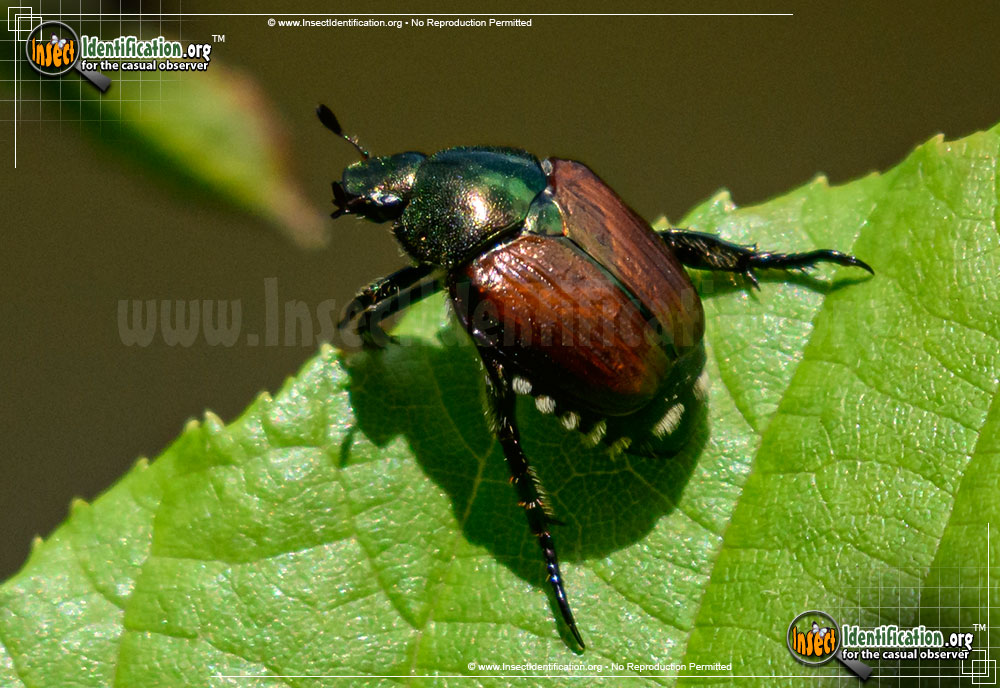

Japanese Beetle Popillia Japonica

These Beetles Are Not Picky Eaters Here S How To Control Them Before They Munch Your Whole Garden Vermont Public Radio

How To Prevent Japanese Beetles Lawn Care Blog Lawn Love

Get Ready For Japanese Beetles Ross Tree Company Denver Colorado

How To Get Rid Of Japanese Beetles Planet Natural

Japanese Beetle Habitat Facts How To Get Rid Of Japanese Beetles Safer Brand

Schedule My Japanese Beetle Treatment Today Rainbow Treecare

Japanese Beetle Life Cycle Youtube

How To Control Japanese Beetles Organically Japanese Beetles Garden Pests Garden Pest Control
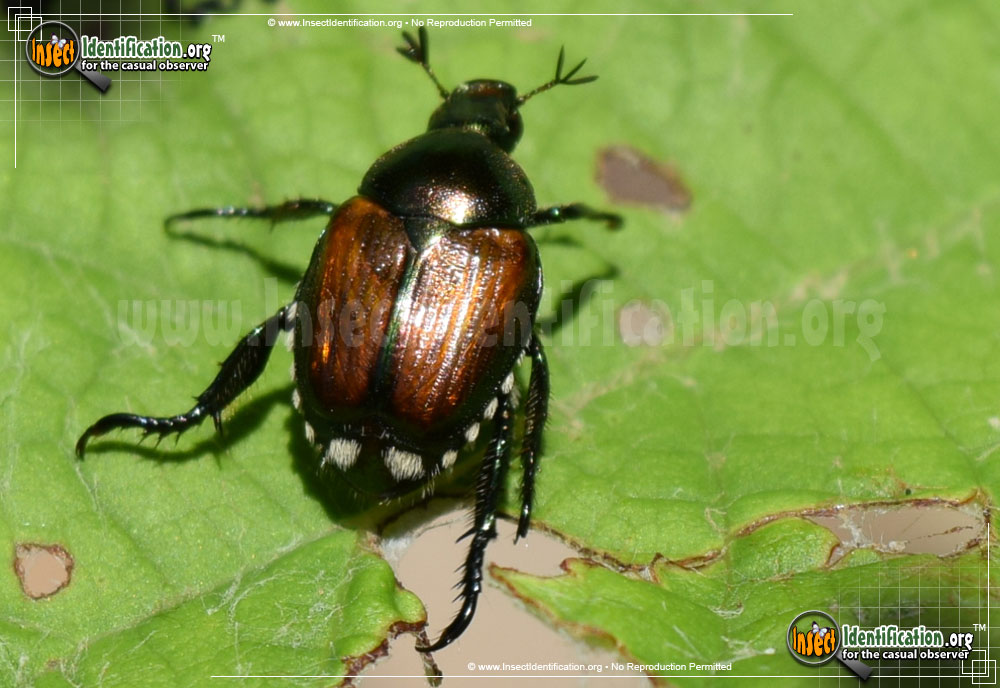

Japanese Beetle Popillia Japonica

Tips On How To Control Japanese Beetles In Colorado
How To Get Rid Of Japanese Beetles Gardener S Path

How To Get Rid Of Japanese Beetles In Your Yard

Japanese Beetle Pests Soybean Integrated Pest Management Ipm Field Crops Purdue University
Colorado Garden Punch List Betty Cahill Japanese Beetle Spring Larvae Control

